Table of contents
- Understanding Risk in Trading
- The Foundation of Risk Management
- Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Risk-to-Reward Ratio
- Psychological Aspect of Risk Management
- Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
- Conclusion
Understanding Risk in Trading
What Is Trading Risk?
Trading risk refers to the potential for financial loss in the pursuit of profit. In trading, risk takes many forms, including market risk (the risk of adverse price movements), leverage risk (amplifying both gains and losses), and liquidity risk (the risk of not being able to exit a trade at the desired price).
The Cost of Ignoring Risk
Ignoring risk can have devastating consequences. Traders who do not manage risk effectively often experience significant losses that can wipe out their trading capital. Understanding and addressing risk is crucial to protecting your investment.
The Foundation of Risk Management
Risk Tolerance
Every trader has a different risk tolerance. It’s essential to assess your comfort level with risk and tailor your trading strategy accordingly. Your risk tolerance should dictate the types of assets you trade, the size of your positions, and your overall approach to trading.
Proper Position Sizing
Determining the right position size is a fundamental aspect of risk management. Never risk more than a small percentage of your total capital on a single trade. Many experienced traders recommend risking no more than 1-2% of your capital on any given trade.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
-
01
Diversification
Diversifying your trading portfolio across different assets or asset classes can help spread risk. If one trade goes sour, the impact on your overall portfolio will be limited. However, remember that over-diversification can lead to diluted profits.
-
02
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order is a predetermined price at which you will exit a losing trade. It’s a powerful tool to limit losses and protect your capital. Set your stop-loss levels based on technical analysis, support, and resistance levels.
-
03
Utilizing Trailing Stops
Trailing stops allow you to lock in profits as a trade moves in your favor. As the price rises, the trailing stop follows, ensuring that if the market reverses, you exit with gains. This tool is valuable for letting winners run while protecting against sudden reversals.
-
03
Managing Leverage
Leverage can amplify both profits and losses. Use leverage cautiously, and be aware of the risks involved. Lower leverage levels are often recommended for novice traders.

Risk-to-Reward Ratio
The Importance of R:R
Risk-to-reward ratio (R:R) measures the potential reward of a trade compared to the risk undertaken. A favorable R:R means that the potential reward is significantly greater than the potential risk. Aim for trades with a minimum R:R of 1:2 or better.
Setting Realistic Targets
Set profit targets based on your analysis and maintain discipline in closing positions when these targets are met. Unrealistic profit expectations can lead to overtrading and excessive risk-taking.
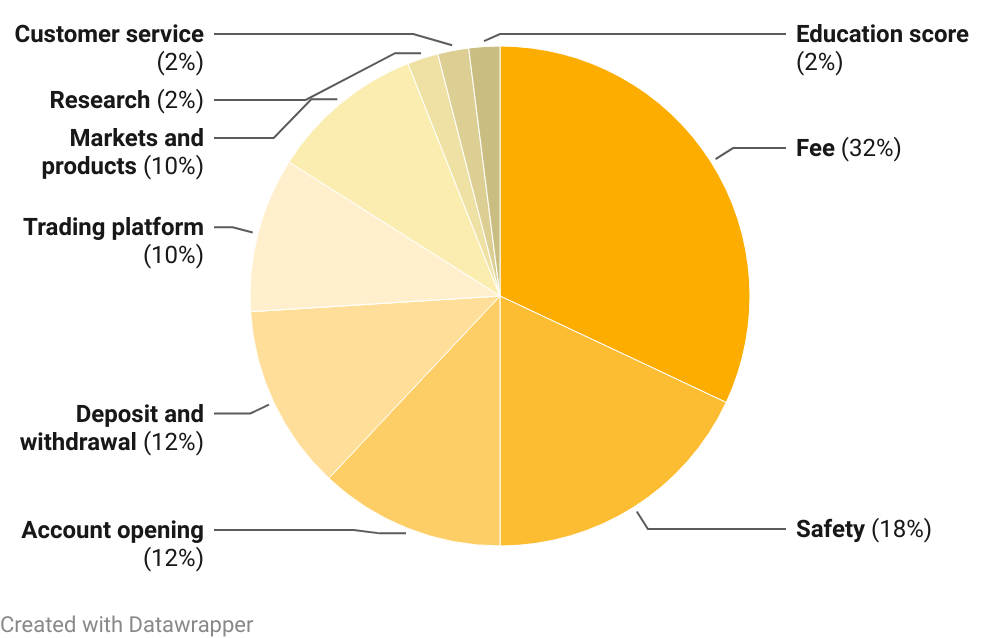
Weight Of Areas In The Methodology
Psychological Aspect of Risk Management
Emotion Management
Fear and greed are common emotions in trading. Emotion-driven decisions can lead to impulsive actions and losses. Develop emotional discipline by sticking to your trading plan and avoiding impulsive changes.
Sticking to Your Plan
A well-thought-out trading plan includes risk management rules. Follow your plan religiously, even when faced with tempting opportunities or stressful situations. Consistency is key to long-term success.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
Regularly Assessing Risk
Market conditions change, and so should your risk management strategy. Regularly review and adjust your risk parameters as needed to adapt to evolving market dynamics.
Adapting to Market Conditions
During periods of high volatility or uncertainty, consider reducing position sizes or tightening stop-loss levels. Conversely, when markets are stable, you may adjust your risk parameters accordingly.
Conclusion
Effective risk management is the cornerstone of successful trading. It’s not about avoiding risk entirely but about managing it intelligently to protect your capital and maximize your chances of profitable trades. By understanding your risk tolerance, employing sound position sizing, and utilizing risk mitigation tools like stop-loss orders and trailing stops, you can navigate the turbulent waters of the financial markets with confidence and discipline. Remember that successful trading is a marathon, not a sprint, and prudent risk management will help you stay in the race for the long haul.Effective risk management is the cornerstone of successful trading. It’s not about avoiding risk entirely but about managing it intelligently to protect your capital and maximize your chances of profitable trades. By understanding your risk tolerance, employing sound position sizing, and utilizing risk mitigation tools like stop-loss orders and trailing stops, you can navigate the turbulent waters of the financial markets with confidence and discipline. Remember that successful trading is a marathon, not a sprint, and prudent risk management will help you stay in the race for the long haul.
