Table of contents
- Table of Contents
- Understanding Forex Trading
- Participants in the Forex Market
- The Mechanics of Forex Trading
- Getting Started with Forex Trading
- Basic Forex Trading Strategies
- Risk Management in Forex Trading
- Advanced Forex Trading Strategies
- Psychology of Forex Trading
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Continuous Learning and Improvement
- Conclusion
Navigating the Forex Markets: A Comprehensive Guide to Forex Trading
Forex trading, short for foreign exchange trading, is a dynamic and decentralized global market where participants exchange currencies. It’s the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. In this blog, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide to forex trading, covering everything from the basics to advanced strategies to help you embark on your forex trading journey.

- What Is Forex?
- How Does the Forex Market Work?
- Major Currency Pairs
Understanding Forex Trading
- Central Banks
- Commercial Banks
- Institutional Investors
- Retail Traders
Participants in the Forex Market
- Currency Quotes
- Bid and Ask Prices
- Lots and Leverage
The Mechanics of Forex Trading
- Setting Up a Forex Trading Account
- Choosing a Reliable Forex Broker
- Selecting the Right Trading Platform
Getting Started with Forex Trading
- Fundamental Analysis
- Technical Analysis
- Sentiment Analysis
Basic Forex Trading Strategies
- Position Sizing
- Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
- Risk-Reward Ratio
Risk Management in Forex Trading
- Carry Trade
- Scalping
- Swing Trading
Advanced Forex Trading Strategies
- Emotions in Trading
- Discipline and Patience
Psychology of Forex Trading
- Overtrading
- Neglecting Risk Management
- Ignoring Fundamentals
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Forex Trading Education
- Keeping a Trading Journal
- Staying Informed About Global Events
Continuous Learning and Improvement
How can we showcase your brokerage?

Understanding Forex Trading
What Is Forex?
Forex, or foreign exchange, refers to the global marketplace where currencies are traded. It involves the simultaneous buying of one currency and selling of another, with the goal of profiting from currency price fluctuations.
How Does the Forex Market Work?
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across different time zones. Currencies are quoted in pairs, with the first currency called the base currency and the second the quote currency. Traders speculate on whether the base currency will appreciate or depreciate relative to the quote currency.
Major Currency Pairs
The most traded currency pairs are known as the majors. These pairs include the EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar), GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar), and USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen).
Participants in the Forex Market
-
01
Central Banks
Central banks, like the Federal Reserve (Fed) in the United States, play a significant role in the forex market through monetary policy decisions that influence exchange rates.
-
02
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are key liquidity providers, facilitating forex transactions for clients and managing their own positions.
-
03
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds and pension funds, participate in forex trading to diversify their portfolios.
-
04
Retail Traders
Individual retail traders, like you, access the forex market through online brokers.

The Mechanics of Forex Trading
Currency Quotes
Currency pairs are quoted with a bid and an ask price. The bid is the price at which you can sell a currency pair, while the ask is the price at which you can buy it.
Bid and Ask Prices
The difference between the bid and ask price is known as the spread. It represents the broker’s profit and is a factor to consider when trading.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds and pension funds, participate in forex trading to diversify their portfolios.
Lots and Leverage
Forex trades are typically conducted in lots, with standard, mini, and micro lot sizes. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital but also increases potential gains and losses.
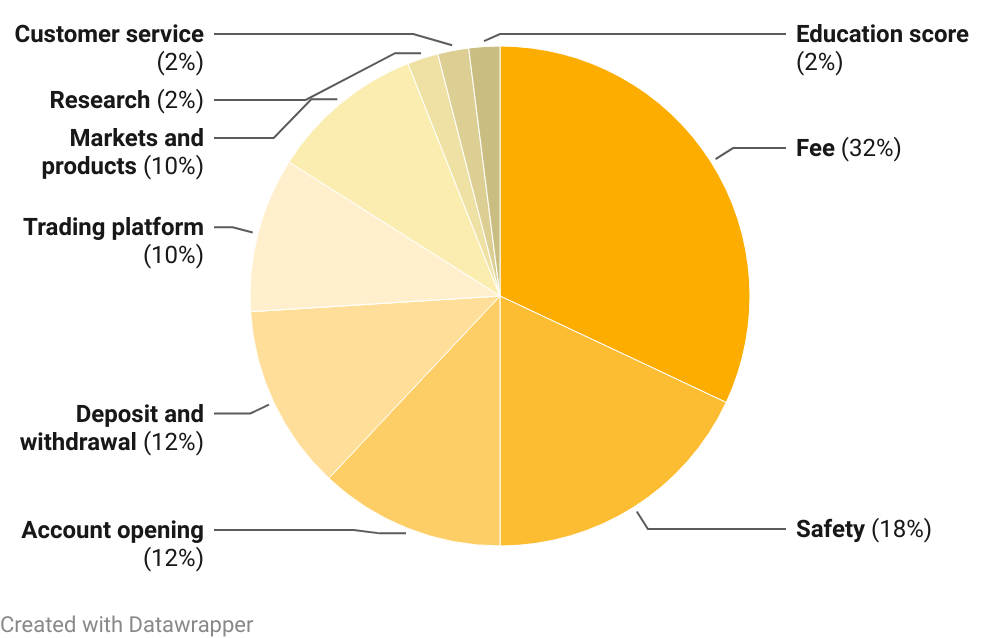
Weight Of Areas In The Methodology
Getting Started with Forex Trading
Setting Up a Forex Trading Account
To start trading forex, you need to open an account with a reputable forex broker.
Choosing a Reliable Forex Broker
Selecting a reliable broker is essential. Look for one with a good reputation, competitive spreads, and a user-friendly trading platform.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds and pension funds, participate in forex trading to diversify their portfolios.
Selecting the Right Trading Platform
A trading platform is your gateway to the forex market. Choose a platform that suits your trading style and provides necessary tools and resources.
Basic Forex Trading Strategies
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves studying economic indicators, geopolitical events, and central bank policies to make trading decisions.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis relies on charts and technical indicators to predict future price movements based on past market behavior.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors, such as hedge funds and pension funds, participate in forex trading to diversify their portfolios.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis gauges market sentiment by examining news sentiment, trader positioning, and social media trends.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
-
01
Position Sizing
Determine the size of your trades based on your risk tolerance and account size. Never risk more than a small percentage of your capital on a single trade.
-
02
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis relies on charts and technical indicators to predict future price movements based on past market behavior.
-
03
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and take-profit orders to lock in profits at predefined levels.
-
04
Risk-Reward Ratio
Ensure that the potential reward of a trade justifies the risk taken. A common rule of thumb is to aim for a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2.

Advanced Forex Trading Strategies
Position Sizing
Determine the size of your trades based on your risk tolerance and account size. Never risk more than a small percentage of your capital on a single trade.
Carry Trade
The carry trade involves borrowing funds in a currency with a low-interest rate and investing in a currency with a higher interest rate, profiting from the interest rate differential.
Scalping
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy where traders aim to make small profits from quick, short-term price movements.
Swing Trading
Swing traders hold positions for several days or weeks, aiming to capture larger price swings within established trends.
Psychology of Forex Trading
Emotions in Trading
Managing emotions, such as fear and greed, is crucial for making rational trading decisions. Emotional discipline is the hallmark of successful traders.
Scalping
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy where traders aim to make small profits from quick, short-term price movements.
Discipline and Patience
Stick to your trading plan, even when faced with challenging market conditions or tempting opportunities. Discipline and patience are virtues in forex trading.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Position Sizing
Determine the size of your trades based on your risk tolerance and account size. Never risk more than a small percentage of your capital on a single trade.
Overtrading
Trading too frequently or with excessively large positions can deplete your capital quickly. Trade with a well-thought-out plan and strategy.
Neglecting Risk Management
Failure to implement proper risk management techniques can lead to significant losses. Always protect your capital.
Ignoring Fundamentals
Both technical and fundamental analysis have their merits. Neglecting one in favor of the other may limit your trading success. A balanced approach is often best.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
Forex Trading Education
Continuous learning is vital in forex trading. Invest time in studying forex strategies, market analysis, and trading psychology.
Overtrading
Trading too frequently or with excessively large positions can deplete your capital quickly. Trade with a well-thought-out plan and strategy.
Keeping a Trading Journal
Maintain a trading journal to record your trades, emotions, and lessons learned. It provides valuable insights for improvement.
Staying Informed About Global Events
Economic and geopolitical events can have a significant impact on forex markets. Stay informed about global news that may affect your trading decisions.
Conclusion
Forex trading is a challenging endeavor, but with dedication and knowledge, it can be highly rewarding. Remember that success in forex trading is not guaranteed, and losses are a part of the game. It’s crucial to approach forex trading with caution, discipline, and a well-thought-out plan.
Continuous learning and experience are the keys to becoming a successful forex trader. So, start small, learn, adapt, and never stop improving your skills in this exciting financial market.
