Table of contents
- Table of Contents
- Understanding Contracts for Difference (CFDs)
- Why Trade CFDs?
- Common Assets for CFD Trading
- Getting Started with CFD Trading
- Strategies for CFD Trading
- Risk Management in CFD Trading
- Regulation and Tax Considerations
- Continuous Learning and Improvement
- Conclusion
Unveiling the World of CFDs in Trading: A Comprehensive Guide
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) have become a popular trading instrument, allowing traders to speculate on the price movements of various assets without owning them. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of CFD trading, discussing what CFDs are, how they work, their advantages and risks, and the strategies and considerations traders should be aware of when using CFDs as part of their trading toolkit.

- What Are CFDs?
- How Do CFDs Work?
- Key Features of CFDs
Understanding Contracts for Difference (CFDs)
- Advantages of CFD Trading
- Potential Drawbacks
Why Trade CFDs?
- Stock CFDs
- Forex CFDs
- Commodity CFDs
- Index CFDs
- Cryptocurrency CFDs
Common Assets for CFD Trading
- Choosing a CFD Broker
- Setting Up a Trading Account
- Risk Management in CFD Trading
Getting Started with CFD Trading
- Day Trading
- Swing Trading
- Hedging
- Leveraged Trading
Strategies for CFD Trading
- Position Sizing
- Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
- Margin and Leverage
Risk Management in CFD Trading
- Regulatory Oversight
- Tax Implications
Regulation and Tax Considerations
- Trading Education
- Keeping a Trading Journal
- Staying Informed About Market Events
Continuous Learning and Improvement
Conclusion
How would we feature you?

Understanding Contracts for Difference (CFDs)
What Are CFDs?
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) are financial derivatives that allow traders to speculate on the price movements of underlying assets without owning the assets themselves. CFDs derive their value from the underlying asset, such as stocks, commodities, currencies, or indices.
How Do CFDs Work?
When trading CFDs, you enter into a contract with a broker, agreeing to exchange the difference in the asset’s price between the contract’s opening and closing. You can profit from both rising and falling markets.
Key Features of CFDs
- Leverage: CFDs allow traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital.
- No Ownership: CFD traders don’t own the underlying asset.
- Diverse Asset Selection: CFDs cover a wide range of assets, providing trading opportunities in various markets.
Why Trade CFDs?
-
01
Advantages of CFD Trading
Diversification: CFDs offer access to a wide range of asset classes.
Leverage: Traders can amplify their potential returns (but also losses) with leverage.
Short Selling: CFDs enable traders to profit from falling markets.
Lower Costs: CFDs typically have lower fees compared to traditional trading.
-
02
Potential Drawbacks
Leverage Risk: High leverage can lead to significant losses.
Counterparty Risk: CFDs are subject to the financial stability of the broker.
Overtrading: The ease of trading CFDs may lead to overtrading if not managed carefully.

Common Assets for CFD Trading
Stock CFDs
Traders can speculate on the price movements of individual stocks without owning the underlying shares.
Forex CFDs
Currency pairs in the foreign exchange market are popular for CFD trading due to high liquidity and 24-hour availability.
Commodity CFDs
CFDs provide access to commodities like oil, gold, and silver, allowing traders to benefit from price fluctuations.
Index CFDs
Traders can speculate on the performance of stock market indices like the S&P 500 or FTSE 100.
Cryptocurrency CFDs
CFDs offer exposure to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum without the need for digital wallets.
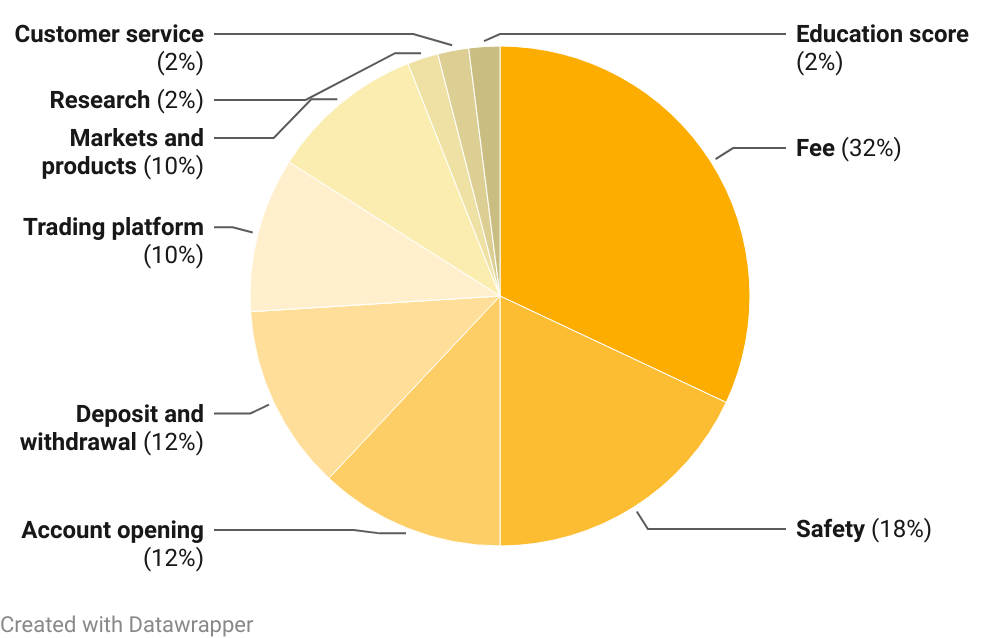
Weight Of Areas In The Methodology
Getting Started with CFD Trading
Choosing a CFD Broker
Select a reputable CFD broker that offers a user-friendly trading platform, competitive spreads, and strong regulatory oversight.
Setting Up a Trading Account
Open a CFD trading account with your chosen broker and fund it with the necessary capital.
Risk Management in CFD Trading
Implement risk management strategies, including position sizing, stop-loss orders, and take-profit orders, to protect your capital.
Strategies for CFD Trading
Day Trading
Day traders aim to profit from short-term price movements within a single trading day. They often use technical analysis and leverage to capitalize on volatility.
Swing Trading
Swing traders hold positions for several days or weeks, seeking to capture price swings within established trends.
Hedging
Traders use CFDs to hedge existing investments, mitigating potential losses in their portfolio.
Leveraged Trading
Leverage can amplify returns, but it also increases risk. Traders must use leverage cautiously and be aware of margin calls.
Risk Management in CFD Trading
-
01
Position Sizing
Determine the size of your CFD positions based on your risk tolerance and account size. Avoid overexposing your capital to a single trade.
-
02
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and take-profit orders to secure profits at predetermined levels.
-
03
Margin and Leverage
Understand the margin requirements and leverage ratios offered by your broker. Monitor your account to avoid margin calls.

Regulation and Tax Considerations
Regulatory Oversight
Ensure your CFD broker is regulated by a reputable financial authority to protect your interests and funds.
Tax Implications
Understand the tax treatment of CFD trading in your jurisdiction. CFD gains may be subject to capital gains tax.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
Trading Education
Invest in trading education to enhance your skills and knowledge. Many online resources and courses are available.
Keeping a Trading Journal
Maintain a trading journal to record your trades, strategies, and lessons learned. This helps improve decision-making and track progress.
Staying Informed About Market Events
Stay updated on economic events, news releases, and market trends that can impact your CFD trading decisions.
Conclusion
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) offer traders a flexible and accessible way to speculate on a wide range of asset classes. While they provide opportunities for profit, CFDs also come with inherent risks, especially due to leverage. Successful CFD trading requires diligent risk management, continuous learning, and discipline.
By understanding the fundamentals of CFDs and implementing sound trading strategies, traders can navigate this dynamic financial instrument with confidence.
